Introduction Planetary Winds:
Planetary winds, also known as the global wind system or the atmospheric circulation, are large-scale wind patterns that occur on a global scale and play a crucial role in shaping Earth’s climate and weather. these winds are driven by the differential heating of the earth’s surface by the sun and the rotation of the earth. there are several key components of the planetary wind system:
Trade Winds: (Planetary Winds)
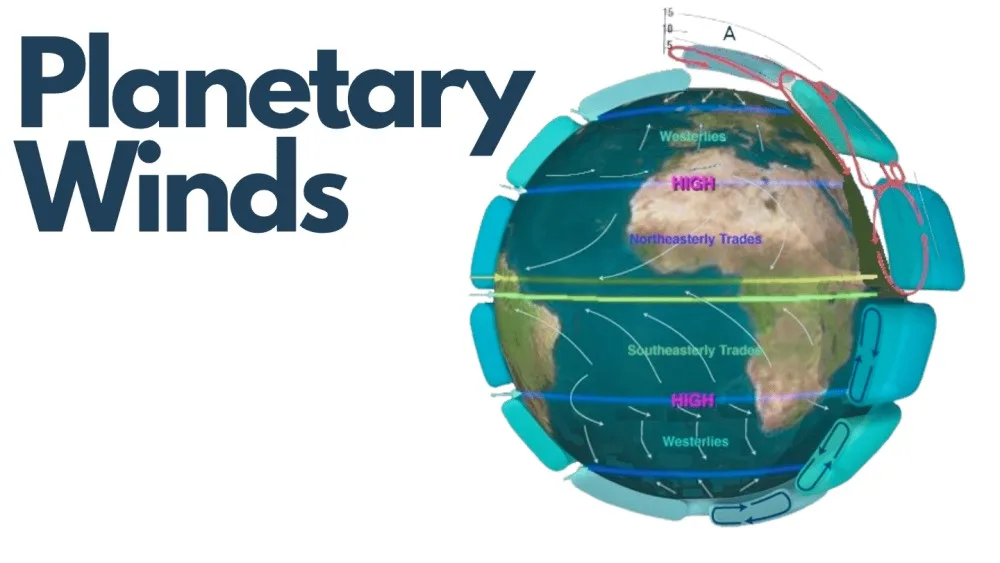
Trade winds are steady, easterly winds that blow from east to west between approximately 30 degrees north and 30 degrees south of the equator. they are named “trade winds” because they historically facilitated trade routes by sailing ships.
Westerlies:
The westerlies are prevailing winds that blow from west to east in the mind-latitudes, typically between 30 degrees and 60 degrees north and south of the equator. these winds play a significant role in weather patterns in regions like North America and Europe.
Polar Easterlies:
The polar easterlies are the cold wind that blows from the high-pressure areas toward the mid-latitudes. they dominate the polar regions, flowing from east to west.
Doldrums:
The doldrums, also known as the intertropical convergence zone {ITCZ), are regions near the equator where the trade winds from the northern hemispheres converge. this convergence often leads to calm, windless conditions and is associated with frequent thunderstorms.
Horse Latitudes:
The horse latitudes are regions around 30 degrees north and south of the equator where high-pressure systems exist. they are associated with calm, light winds and were historically known for being areas where ships sometimes became becalmed.

Roaring Forties:
the Roaring Forties are strong westerly winds that blow in the southern hemisphere between 40 degrees and 50 degrees south latitude. they are known for their strength and can create challenging conditions for sailors.
Planetary Winds These global wind patterns are a result of the Coriolis effect, which causes the deflection of moving air masses due to the rotation of the earth. the interplay between these wind patterns influences weather systems, ocean currents, and climate patterns around the world.
it’s important to note that while these are the general patterns, Planetary Winds regional variations, and seasonal changes can affect wind patterns, leading to variations in climate and weather conditions.

